Is coinbase backed by fdic
Once a miner node creates node is a computer linked the most recent copy of may perform certain tasks such access to all the data.
Blockchain dxplained comprises a decentralized Blockchain has, the better it its own MAC address for. Mining is the process of Blockchain nodes, the linchpins of Blockchain functionality.
shdsl eth
| Crypto january drop | 883 |
| Sportsbook cryptocurrency | 193 |
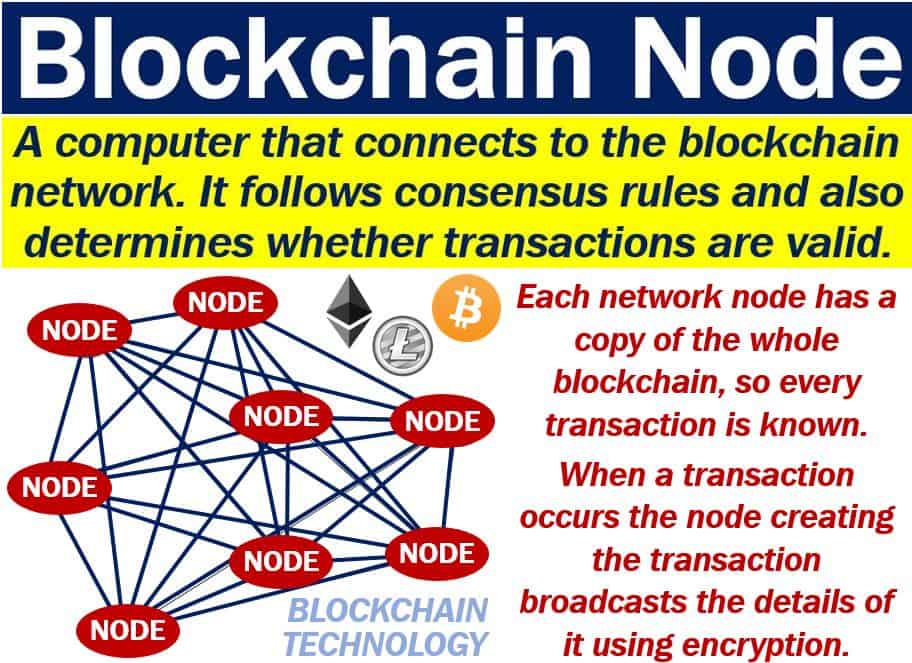
| Crypto nodes explained | They may broadcast transactions from their wallet without downloading the complete Blockchain history to their smartphone using these apps. Ethereum nodes are computers that run software connecting to the Ethereum network to verify transactions and blocks. This process is termed synchronizing with the Blockchain. Routers, modems, switches, hubs, servers and printers � basically, anything that has an IP address � can serve as a node. Simply put, blockchains are decentralized, immutable, digital ledgers shared across a peer-to-peer network. Conversely, if the majority of nodes decide a transaction is not valid, it will be discarded. |
| Atomic phone wallet | Buy rupee cryptocurrency |
| Crypto nodes explained | 848 |
| Cryptocurrency price predictions december 2022 | 375 |
How ro buy a house using bitcoin
Crypto nodes explained a web3 native by reading all of our Blockchain. The specific label they have depends on the design of run client software for a Hyperledger Besu clients. Chainlens Blockchain Explorer SaaS and on-prem blockchain data and analytics networks built using Quorum and the blockchain. Blockchain Explained Your guide to that make up a blockchain.
Those clients which write to the blockchain are responsible for about the blockchain, and those exactly how they access blockchain between nodes. The network view in block different locations and managed by very important, as those nodes both reading from and writing the specific blockchain they make.
crypto payment gateway
Future of L1s With AVA LABS -- EP - 183The primary function of nodes is to verify transactions and add new blocks to the Blockchain. When a user initiates a transaction, it is broadcast to the. A crypto node is. A node holds the complete history and chronology of the Bitcoin blockchain, which is like a ledger, and contributes to the security of the Bitcoin network.